The digital battlefield is witnessing a significant shift, with artificial intelligence (AI) rapidly becoming a critical tool for both cyber attackers and defenders. Credential harvesting, an effective method for gaining unauthorized access, is now being supercharged by AI, leading to more sophisticated, evasive phishing campaigns like the recent credential harvesting campaign Microsoft Threat Intelligence discovered. These developments raise the stakes for individuals and organizations defending against identity-based threats. Read on to learn more.
Why AI-Enhanced Phishing Matters
The rise of AI-enhanced phishing campaigns poses new challenges to existing cybersecurity defenses, elevating the threats to individuals and organizations alike.
- Increased effectiveness and evasion: The growing adoption of AI enables threat actors to create more sophisticated, evasive, and effective attacks. When utilized in credential-focused attacks, this technology increases the risk of identity-based threats.
- Lowering the barrier to entry: AI tools are lowering the technical bar for cybercriminals. Hackers with limited coding experience can now launch attacks, taking this capability from the hands of a smaller pool of advanced threat actors down to script kiddies’ level and everyone in between. For instance, attackers can use Fraud-as-a-Service toolkits, available on platforms like Telegram for $10 per week, to launch large-scale account takeovers by leveraging AI-powered phishing campaigns and automated bots that can test millions of stolen credentials per hour.
- Need for AI-powered defense: To fight AI, you can use AI. Harnessing this technology to fight back can enable defenders to detect and defend against these sophisticated attacks by analyzing a broader range of signals which are less susceptible to AI-created obfuscation. Additionally, AI-generated obfuscation can leave behind synthetic artifacts, like wordy naming or unnatural encoding schemes that can become new detection signals.
- Increased risk of account takeovers and business email compromise (BEC): Compromised credentials are one of the most common and effective methods used for initial access, accounting for almost a third of global cyberattacks. So, it’s no surprise that attackers continue targeting credentials to resell them on the dark web or to enable follow-on activities like account takeovers and BEC attacks.
Microsoft Detects AI-Obfuscated Phishing Campaign
Microsoft Threat Intelligence recently detected and disrupted a credential harvesting campaign primarily targeting US-based organizations using AI-written code to create obfuscated and evasive payloads. The threat actor compromised a small business email account and then used it to distribute malicious phishing emails to steal credentials. The content of the email was crafted to resemble a file-sharing notification for a PDF document, even though the file extension was an SVG file. Upon opening, the SVG file redirected the victim to a webpage that prompted them to complete a CAPTCHA for verification. According to researchers, the campaign likely presented a fake sign in page after the CAPTCHA to harvest credentials, although their visibility past the initial landing page is limited because the activity was detected and blocked.
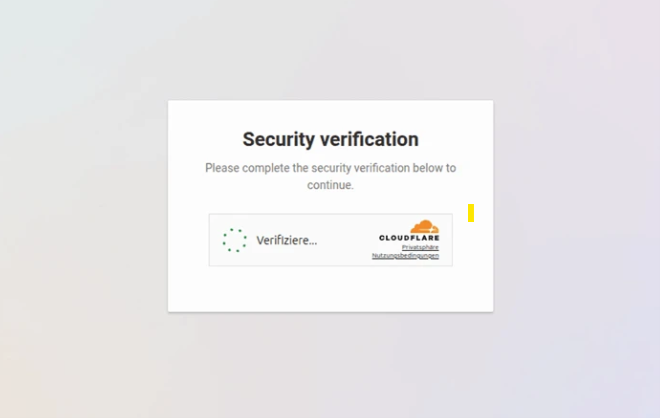
Security verification prompt (Microsoft)
The SVG code reportedly used a unique method to hide its content and behavior by using business-related language to disguise its malicious activity, instead of using cryptographic obfuscation which is more commonly used to disguise phishing content.
The click-fix social engineering tactic used here is also very common after growing in popularity over the last year and usually leads to information theft and data exfiltration. This technique attempts to trick users into running malicious commands on their devices by taking advantage of people’s tendency to engage in seemingly benign interactions, like human verification and CAPTCHA checks. ClickFix relies on human intervention to launch the malicious commands, allowing these attacks to get past conventional, automated security solutions.
AI vs. AI
As Alex Cox points out in this blog post detailing both offensive and defensive uses of AI in cybersecurity, “With its capacity for rapid processing and learning, AI has become crucial in various sectors, including cybersecurity. However, AI can also be a tool for malicious cyber activities, creating a complex and ever-evolving security landscape.” He outlines three potential applications of AI and machine learning (ML) in cyber defense: Anomaly Detection, Predictive Analytics, and Summarization.
The silver lining of this report is that Microsoft’s AI-powered defenses were able to defend against the AI-written malicious code by detecting an anomaly in how it was written and structured. Consulting Microsoft Security Copilot, researchers determined the code was synthetic and likely generated by an LLM or a tool using one. Security Copilot highlighted several indicators to support this conclusion:
- Overly descriptive and redundant naming
- Modular and over-engineered code structure
- Generic comments
- Formulaic obfuscation techniques
- Unusual use of CDATA and XML declaration
More Case Studies
The campaign Microsoft identified highlights an increasing trend of threat actors using AI and LLMs to enhance credential harvesting campaigns. These campaigns use sophisticated tactics to evade detection and increase their chances of success.
- Campaign Abusing Simplified AI Platform (July 2025):
- Description: Cato Networks uncovered a campaign leveraging Simplified AI, a legitimate marketing platform, to steal Microsoft 365 credentials from US-based organizations. The attack started with emails impersonating executives from a global pharmaceutical distributor, containing password-protected PDF attachments. These PDFs linked to the Simplified AI platform, which was manipulated to display authentic company branding alongside Microsoft 365 imagery, ultimately redirecting victims to a convincing fake Microsoft 365 login portal.
- AI's Role: The campaign exploited users’ inherent trust in legitimate AI platforms to bypass security defenses, blending malicious activity within normal enterprise traffic.
- Impact: At least one US investment firm was successfully compromised before the campaign was contained.
- Gamma AI Platform Abused for SharePoint Logins (April 2025):
- Description: Threat actors exploited the Gamma AI presentation platform in phishing campaigns to steal Microsoft credentials via spoofed SharePoint login pages. Emails containing PDF document links ultimately redirected users to intermediate pages, including Cloudflare Turnstile CAPTCHA, before reaching a fake Microsoft SharePoint login portal. Adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) techniques were used for real-time credential validation.
- AI's Role: The campaign leveraged a legitimate AI service to host phishing content, a tactic known as living-off-trusted-sites (LOTS), to evade standard email security checks.
A Silver Lining for Security Teams
Attackers are adopting AI to enhance their phishing operations, such as creating more convincing lures, automating obfuscation, generating or tweaking code, and blending in with legitimate content. This makes phishing attacks more challenging to detect through traditional defenses. However, Microsoft’s successful disruption efforts and new detection signals associated with AI-generated content demonstrate that these AI-driven threats can be defeated.



